目次
(0)ggplot2による描画の概略
- [PDF]|ggplot2による描画の概略
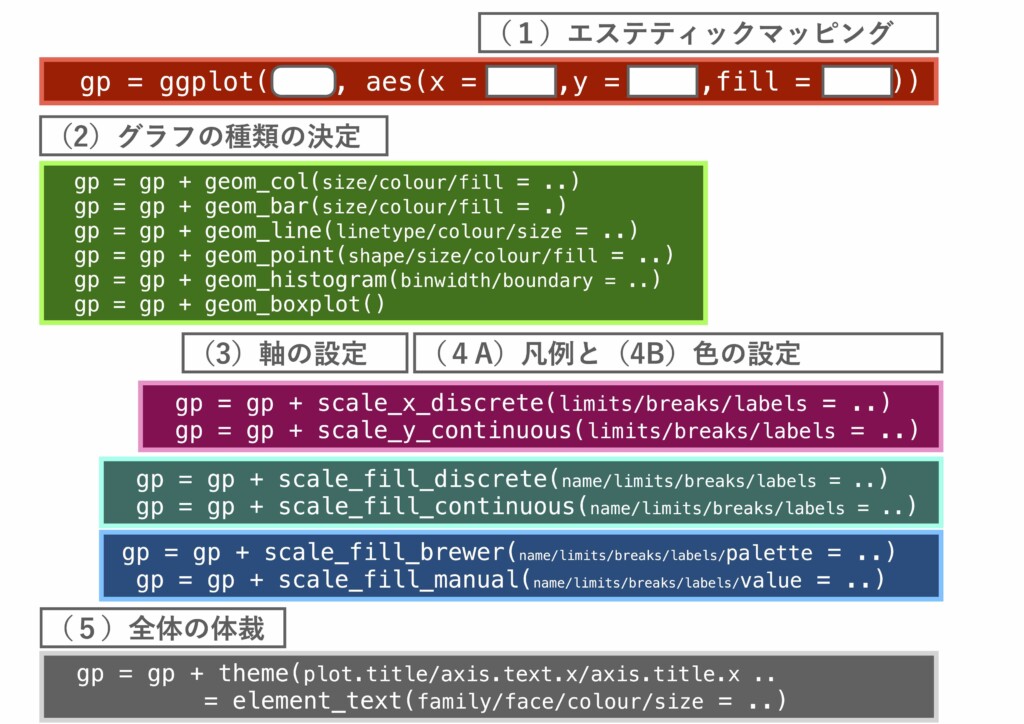
#準備
# ggpplot2ライブラリを使えるようにします
install.packages("ggplot2")
library(ggplot2)
# gcookbookライブラリを使えるようにします
install.packages("gcookbook")
library(gcookbook)
# 例えば以下のようなデータフレームが使えます。
head(heightweight)
#. sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb
#1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0
#2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0
#3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0
#4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0
#5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5
#6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0
#(1)エステティックマッピング
## x軸に年齢、y軸に身長、fill属性に性別を割り振る ## この時点では何のグラフも出力されません gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn,fill=sex)); gp
#(2)散布図としてグラフ化する
gp = gp + geom_point(shape=21,size=6); gp
#(3)軸の設定
gp = gp + scale_x_continuous(limits=c(10,20),breaks=c(10,15,20)); gp gp = gp + scale_y_continuous(limits=c(0,100),breaks=c(0,50,100)); gp
#(4A)凡例の設定
gp1 = gp + scale_fill_discrete(name = "Gender", labels=c("Female","Male")); gp1
#(4B)凡例と色の設定
gp1 = gp + scale_fill_grey(name = "Gender", labels=c("Female","Male"),
start=0.2, end=0.8); gp1
gp1 = gp + scale_fill_brewer(name = "Gender", labels=c("Female","Male"),
palette="Set2"); gp1
#(5)全体の体裁の設定
gp2 = gp1 + theme(
legend.title = element_text(size = 30),
axis.title.x = element_text(size = 30),
axis.title.y = element_text(size = 30),
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 20),
axis.text.y = element_text(size = 20),
legend.text = element_text(size=20)
);gp2
(1)各種のグラフ
棒グラフ [geom_col]
#デフォルトの出力
# gcookbookのライブラリを使います
# インストールが済んでいない人は
# install.packages("gcookbook")を実行
library(gcookbook)
# 使用するデータフレーム
BOD
#Time demand
#1 1 8.3
#2 2 10.3
#3 3 19.0
#4 4 16.0
#5 5 15.6
#6 7 19.8
# 基本レイヤを作成
## この時点では何も出力されません
gp = ggplot(BOD,aes(x=Time,y=demand))
# デフォルトの棒グラフ(塗りは黒、幅は0.9)
gp + geom_col()
# 棒グラフの塗りつぶしを白、枠線を黒とし、枠線のサイズを0.2とする。
gp + geom_col(fill="white",colour="black", size=0.2)
# 棒グラフの幅を最大幅の半分とする(デフォルトは0.9)
gp + geom_col(width=0.5)
#属性の要素ごとに分ける方法
library(gcookbook)
cabbage_exp
#. Cultivar Date Weight sd n se
#1 c39 d16 3.18 0.9566144 10 0.30250803
#2 c39 d20 2.80 0.2788867 10 0.08819171
#3 c39 d21 2.74 0.9834181 10 0.31098410
#4 c52 d16 2.26 0.4452215 10 0.14079141
#5 c52 d20 3.11 0.7908505 10 0.25008887
#6 c52 d21 1.47 0.2110819 10 0.06674995
# 基本レイヤを作成
## x軸をData、y軸をWeight、塗りをCultivarにマッピング
gp = ggplot(cabbage_exp,aes(x=Date,y=Weight,fill=Cultivar))
# デフォルトはfillを積み上げる(棒グラフ)
gp + geom_col()
# 引数で「積み上げ」を明示的に指定
gp + geom_col(position = position_stack())
## 積み上げ順序の反転
gp + geom_col(position = position_stack(reverse = TRUE))
# 100%積み上げ棒グラフとする
gp + geom_col(position = "fill")
# 水平方向に並べる(棒グラフ)
## デフォルトはfill属性同士はぴたりと張り付く
gp + geom_col(position = position_dodge())
# 幅を0.7とし、隙間を0.1だけ空ける。
## この場合、幅に隙間を足した値をposition_dodgeの引数に与える
gp + geom_col(position = position_dodge(0.8),width=0.7)
gp + geom_col(position = position_dodge(0.72),width=0.7) #隙間を狭める
# fillではなくinteractionを使っても同じことができます
# fillではなくinteractionを使っても同じことができます
gp = ggplot(cabbage_exp,aes(x=interaction(Date,Cultivar),
y=Weight,fill=Cultivar))
gp + geom_col()
#エラーバーの作成
# cabbage_expより、Cultivarがc39のものだけ取り出す
cabbage_exp0 = cabbage_exp[cabbage_exp$Cultivar=="c39",]
# Cultivar Date Weight sd n se
#1 c39 d16 3.18 0.9566144 10 0.30250803
#2 c39 d20 2.80 0.2788867 10 0.08819171
#3 c39 d21 2.74 0.9834181 10 0.31098410
gp0 = ggplot(cabbage_exp0,aes(x=Date,y=Weight))
gp1 = gp0 + geom_col(fill="white",colour="black")
# エラーバーの作成(widthはエラーバーの横幅)
gp1 + geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=Weight-se,ymax=Weight+se),width=.2)
# 横ならびタイプ(dodge)でエラーバーを追加する時
## 棒グラフのデフォルトのずらし幅(0.9)に合わせる。
gp + geom_col(position = position_dodge()) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=Weight-se,ymax=Weight+se),
position=position_dodge(0.9), width=.2)
棒グラフ(数え上げ) [geom_bar]
#同じ値のものを数え上げる
library(gcookbook)
# mtcarsの最初の6行を表示
head(mtcars)
# mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
#Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
#Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
#Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
#Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
#Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2
#Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1
# 列名cylのデータを確認
mtcars$cyl
#[1] 6 6 4 6 8 6 8 4 4 6 6 8 8 8 8 8 8 4 4 4 4 8 8 8 8 4 4 4 8 6 8 4
# 各要素の数を数える
table(mtcars$cyl)
# 4 6 8
#11 7 14
# 列名cylをカテゴリカル変数に変更し、
# 各要素の個数を数え上げて棒グラフとして表示
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=factor(cyl))) + geom_bar()
# factorにしない場合、X軸のラベルに5と7も表示されることに注意
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=cyl)) + geom_bar()
# 数え上げた個数を棒グラフ上に表示
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=factor(cyl))) + geom_bar() +
geom_text(aes(label=..count..),stat="count",
vjust=1.5,colour="white")
#属性の要素ごとに分ける方法
# 列名cylのデータを確認
mtcars$gear
#[1] 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 4 5 5 5 5 5 4
table(mtcars[,c("cyl","gear")])
# gear
#cyl 3 4 5
# 4 1 8 2
# 6 2 4 1
# 8 12 0 2
# 変数cylと変数gearの組み合わせについて、gearで色分け
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=interaction(cyl,gear),fill=factor(gear))) + geom_bar()
# 変数cylで色分け
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=interaction(cyl,gear),fill=factor(cyl))) + geom_bar()
# fillにマッピングされた変数(数値)をファクタにしない場合、
# 連続値として扱われ、カラーバーで色付けされることに注意
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=interaction(cyl,gear),fill=gear)) + geom_bar()
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=interaction(cyl,gear),fill=cyl)) + geom_bar()
# interactionを使わない方法の例
## デフォルトは積み上げ
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=cyl,fill=factor(gear))) + geom_bar()
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=gear,fill=factor(cyl))) + geom_bar()
## 引数にposition=position_dodge()で横並びにする
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=cyl,fill=factor(gear))) + geom_bar(position=position_dodge())
ggplot(mtcars,aes(x=gear,fill=factor(cyl))) + geom_bar(position=position_dodge())
折れ線グラフ [geom_line]
#基本
library(gcookbook) BOD #Time demand #1 1 8.3 #2 2 10.3 #3 3 19.0 #4 4 16.0 #5 5 15.6 #6 7 19.8 # 基本レイヤの出力 gp = ggplot(BOD,aes(x=Time,y=demand)) # デフォルトのグラフ gp + geom_line() # 線の色を深緑にして、線の太さを1.5とする。 gp + geom_line(colour = "dark green",size=1.5) # 線を点線とする。 gp + geom_line(linetype="dashed") # xをファクタにすると、カテゴリカルな系列と解釈され、 # x軸の6が取り除かれます。 ## aes(group=1)は、Timeが同じグループに属していることを ## 明示しています。(無いとエラーとなります) gp = ggplot(BOD,aes(x=factor(Time),y=demand,group=1)) gp + geom_line()
#属性の要素ごとに分ける方法
library(gcookbook) tg #. supp dose length #1 OJ 0.5 13.23 #2 OJ 1.0 22.70 #3 OJ 2.0 26.06 #4 VC 0.5 7.98 #5 VC 1.0 16.77 #6 VC 2.0 26.14 # 基本レイヤの作成 gp = ggplot(tg,aes(x=dose,y=length,colour=supp)) # suppの要素(OJ、VC)ごとに、色分けして出力 gp + geom_line() # 線の描画をグループ間で左右に0.2だけずらす gp + geom_line(position = position_dodge(0.2)) # 同じ位置に点を重ねる gp + geom_line(position = position_dodge(0.2)) + geom_point(position=position_dodge(0.2),shape=21,size=5,fill="white") # suppをlinetypeでマッピング ggplot(tg,aes(x=dose,y=length,linetype=supp)) + geom_line()
#エラーバーの描画
library(gcookbook)
cabbage_exp
#. Cultivar Date Weight sd n se
#1 c39 d16 3.18 0.9566144 10 0.30250803
#2 c39 d20 2.80 0.2788867 10 0.08819171
#3 c39 d21 2.74 0.9834181 10 0.31098410
#4 c52 d16 2.26 0.4452215 10 0.14079141
#5 c52 d20 3.11 0.7908505 10 0.25008887
#6 c52 d21 1.47 0.2110819 10 0.06674995
# ドッジの設定を変数に保存
pd = position_dodge(0.3)
# Cultivarの要素に基づき、折れ線グラフを分けて描画
# 折れ線に関して、Cutivarでグループ分けすることを
# 明示的に伝える必要がある(colourをerrorbarでも使っているため)
gp = ggplot(cabbage_exp,
aes(x=Date,y=Weight,colour=Cultivar,group=Cultivar))
# エラーバーの描画
gp + geom_errorbar(
aes(ymin=Weight-se,ymax=Weight+se),
width=.2,size=0.25,colour="black",position=pd) +
geom_line(position=pd) +
geom_point(position=pd,size=5)
散布図 [geom_point]
#基本
library(gcookbook) # heightweightの最初の6行 head(heightweight) #. sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb #1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0 #2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0 #3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0 #4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0 #5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5 #6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0 # 基本レイヤ gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn)) # デフォルトの散布図を出力 gp + geom_point() # 正方形の点(22)、サイズを3、塗りつぶしの色を白に gp + geom_point(shape=22, size = 3, fill = "white") # 点の枠線をdarkredにする(他は上を参照)。 gp + geom_point(shape=22, size = 4, colour="darkred", fill = "white")
#グループ分け
library(gcookbook) # heightweightの最初の6行 head(heightweight) #. sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb #1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0 #2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0 #3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0 #4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0 #5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5 #6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0 # 性別(sex)で色分け gp_col = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn,colour=sex)) gp_col + geom_point() # 性別(sex)で形状を変える gp_shape = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn,shape=sex)) gp_shape + geom_point() # 性別(sex)で色も形も変える gp_colshape = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn,colour=sex,shape=sex)) gp_colshape + geom_point(size=5)
ヒストグラム [geom_histogram]
#基本
library(gcookbook)
# faithfulの最初の6行
head(faithful)
# eruptions waiting
#1 3.600 79
#2 1.800 54
#3 3.333 74
#4 2.283 62
#5 4.533 85
#6 2.883 55
# 基本レイヤ
gp = ggplot(faithful,aes(x=waiting))
# デフォルトのヒストグラム
gp + geom_histogram()
# ヒストグラムの塗りつぶしの色を白に、枠線の色を黒とする。
gp + geom_histogram(fill="white",colour="black")
# ビン幅を8に、ビンの開始を31とする。
# [31~39), [39~47), [47~55), ...(最大はデータによる)
gp + geom_histogram(binwidth=8, boundary = 31,
fill="white",colour="black")
# ビン幅を[31~39), [39~47), [47~55), ...[87~95)とする
gp + geom_histogram(breaks = seq(31,95,by=8),
fill="white",colour="black")
#グループ分け
library(dplyr) library(MASS) # faithful(出生時体重)の最初の6行 head(birthwt) # low age lwt race smoke ptl ht ui ftv bwt #85 0 19 182 2 0 0 0 1 0 2523 #86 0 33 155 3 0 0 0 0 3 2551 #87 0 20 105 1 1 0 0 0 1 2557 #88 0 21 108 1 1 0 0 1 2 2594 #89 0 18 107 1 1 0 0 1 0 2600 #91 0 21 124 3 0 0 0 0 0 2622 # smoke=0:喫煙なし # smoke=1:喫煙あり # bwt:出生児体重 # 喫煙の有無ごとにヒストグラムを分けて描画 gp = ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=bwt,fill=factor(smoke))) ## デフォルトでは積み上げで表示 gp + geom_histogram() ## 横並びではよくわからない gp + geom_histogram(position=position_dodge()) ## 重ねて表示(半透明とする) gp + geom_histogram(position=position_identity(),alpha=0.6) # ファセット(facet_grid)を使うと、 # グループごとに異なるグラフで描画をしてくれる ## facet_grid関数の引数に、グループ分けしたい変数を指定 ## 書式:facet_grid(XXX ~ .) # 喫煙の有無(smoke)でグループ分け gp = ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=bwt)) gp + geom_histogram(fill="white",colour="black") + facet_grid(smoke ~ .) # 人種(race)でグループ分け gp + geom_histogram(fill="white",colour="black") + facet_grid(race ~ .)
箱ひげ図 [geom_boxplot]
#基本
library(dplyr) library(MASS) # faithful(出生時体重)の最初の6行 head(birthwt) # low age lwt race smoke ptl ht ui ftv bwt #85 0 19 182 2 0 0 0 1 0 2523 #86 0 33 155 3 0 0 0 0 3 2551 #87 0 20 105 1 1 0 0 0 1 2557 #88 0 21 108 1 1 0 0 1 2 2594 #89 0 18 107 1 1 0 0 1 0 2600 #91 0 21 124 3 0 0 0 0 0 2622 # race(人種)は1,2,3のいずれか table(birthwt$race) # 1 2 3 #96 26 67 # 基本レイヤの作成 ## race(人種) をファクタに変換 gp = ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(race),y=bwt)) # デフォルトの箱ひげ図 gp + geom_boxplot() # 外れ値の範囲設定(IQR x 1.5)および、描画の形 gp + geom_boxplot(outlier.size=1.5, outlier.shape = 21) # 外れ値を表示しない ## dotplotを重ね書きするときには表示しないのがよい gp + geom_boxplot(outlier.shape = NA) # birthwtの全ての行を対象に箱ひげ図を作成 ## xに任意の値を与える(下の場合1) ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=1,y=bwt)) + geom_boxplot() ## x軸の目盛とラベルを除く ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=1,y=bwt)) + geom_boxplot() + scale_x_continuous(breaks=NULL) + theme(axis.title.x = element_blank())
#N x Mの箱ヒゲ図
library(dplyr)
library(MASS)
# faithful(出生時体重)の最初の6行
head(birthwt)
# low age lwt race smoke ptl ht ui ftv bwt
#85 0 19 182 2 0 0 0 1 0 2523
#86 0 33 155 3 0 0 0 0 3 2551
#87 0 20 105 1 1 0 0 0 1 2557
#88 0 21 108 1 1 0 0 1 2 2594
#89 0 18 107 1 1 0 0 1 0 2600
#91 0 21 124 3 0 0 0 0 0 2622
# smoke(喫煙の有無: 0,1)
# race(人種:1,2,3)
# smoke x raceは合計6種類
table(birthwt[,c("race","smoke")])
# smoke
#race 0 1
# 1 44 52
# 2 16 10
# 3 55 12
# 上記の6つのグループそれぞれで箱ひげ図を出力
# smokeで色分けする場合(いずれもファクタに変換する)
ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(race),y=bwt,fill=factor(smoke))) +
geom_boxplot()
## 凡例ラベルの表記を変更
ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(race),y=bwt,fill=factor(smoke))) +
geom_boxplot() +
scale_fill_discrete(labels=c("NO SMOKE","SMOKE"))
# raceで色分けする場合
ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(smoke),y=bwt,fill=factor(race))) +
geom_boxplot()
#dotplotを重ねて描画
library(dplyr)
library(MASS)
# faithful(出生時体重)の最初の6行
head(birthwt)
# low age lwt race smoke ptl ht ui ftv bwt
#85 0 19 182 2 0 0 0 1 0 2523
#86 0 33 155 3 0 0 0 0 3 2551
#87 0 20 105 1 1 0 0 0 1 2557
#88 0 21 108 1 1 0 0 1 2 2594
#89 0 18 107 1 1 0 0 1 0 2600
#91 0 21 124 3 0 0 0 0 0 2622
# 基本レイヤの作成
gp = ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(race),y=bwt))
# ビンをY軸上に区切って(ビン幅:50)ドットをX軸方向に積み上げる
# デフォルトは棒グラフの中心から右に配列される
gp + geom_boxplot() +
geom_dotplot(binaxis="y", binwidth=50)
# 中央寄せとして、色を中抜きとする。
gp + geom_boxplot() +
geom_dotplot(binaxis="y", binwidth=50,
stackdir="center", fill=NA)
# 平均値の追加(stat_summaryを使用する)
gp + geom_boxplot() +
geom_dotplot(binaxis="y", binwidth=50,
stackdir="center", fill=NA) +
stat_summary(fun.y="mean",geom="point",
shape=23,size=5,fill="red")
# N x Mの箱ひげ図でdotplotを重ねる
## smoke=0を白に、smoke=1を灰色にマッピング
## (boxplotとdotplotとstat_summaryのfillを個別に設定できればよいが
## やり方わからず、わかる人いたらご教示ください)
ggplot(birthwt,aes(x=factor(race),y=bwt,fill=factor(smoke))) +
geom_boxplot() +
scale_fill_manual(values=c("white","gray"),
labels=c("NO SMOKE","SMOKE")) +
geom_dotplot(binaxis="y", binwidth=35,
stackdir="center",
position = position_dodge(0.75)) +
stat_summary(fun.y="mean",geom="point",
shape=23,size=5,
position = position_dodge(0.75))
(2)軸の設定
#使用するデータフレーム
library(gcookbook) head(heightweight) #. sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb #1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0 #2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0 #3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0 #4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0 #5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5 #6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0 str(heightweight) #'data.frame': 236 obs. of 7 variables: #$ sex : Factor w/ 2 levels "f","m": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... #$ ageYear : num 11.9 12.9 12.8 13.4 15.9 ... #$ ageMonth : int 143 155 153 161 191 171 185 142 160 140 ... #$ heightIn : num 56.3 62.3 63.3 59 62.5 62.5 59 56.5 62 53.8 ... #$ weightLb : num 85 105 108 92 112 ... #$ ageYearf : Factor w/ 7 levels "11","12","13",..: 1 2 2 3 5 4 5 1 3 1 ... #$ ageYear.f: Factor w/ 7 levels "11","12","13",..: 1 2 2 3 5 4 5 1 3 1 ...
#軸タイトル(name)
library(gcookbook)
# 散布図を描画(xを年齢、yを身長)
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn))
gp = gp + geom_point()
# x軸・y軸のタイトルを設定しなおす
## デフォルトではデータフレームの列名が使われる。
gp + xlab("Age Year") + ylab("Height")
## 別の方法(1)
gp + labs(x="Age Year", y = "Height")
## 別の方法(2)
## scale_xy_continuousは連続値変数を扱う軸の設定
gp + scale_x_continuous(name = "Age Year") +
scale_y_continuous(name = "Height")
## x軸のタイトルを非表示にする
gp + xlab(NULL)
gp + scale_x_continuous(name=NULL)
# x軸の目盛とラベルを除く
gp + scale_x_continuous(breaks = NULL)
#目盛と範囲の設定(連続値変数) [scale_x_continuous][scale_y_contnuous]
#breaks(目盛)・limits(範囲)・labels(目盛に対応するラベル)
#breaks(目盛)・limits(範囲)・labels(目盛に対応するラベル)
library(gcookbook)
# 散布図を描画(xを年齢、yを身長)
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn))
gp = gp + geom_point()
# x軸の目盛を1刻みとする(範囲では無い)
gp + scale_x_continuous(breaks = 10:20)
# x軸の範囲を0〜20とする。
gp + scale_x_continuous(limits=c(10,20))
# x軸の目盛と範囲を同時に変える。
gp + scale_x_continuous(breaks=seq(10,20,by=2),limits=c(10,20))
# y軸の目盛と範囲を同時に変える。
gp + scale_y_continuous(breaks=seq(0,100,by=10),limits=c(0,100))
# xim、ylimを使っても同じ
gp + xlim(10,20) + ylim(40,80)
gp + xlim(10,20) + ylim(80,40) #y軸を反転
## y軸の反転(および範囲の設定)
gp + scale_y_reverse(limits=c(80,40))
# データの内容から軸の範囲を決定
gp + xlim(min(heightweight$ageYear)-2,
max(heightweight$ageYear)+2) +
ylim(min(heightweight$heightIn)-5,
max(heightweight$heightIn)+5)
# 横軸が「y=0」を含む様に拡大
gp + expand_limits(x=0)
# 任意に設定した目盛の位置に位置にラベルを打つ
gp + scale_y_continuous(breaks=c(50,56,60,72),
labels=c("Tiny","Short","Medium","Tallish"))
#離散値変数の軸設定 [scale_x_discrete][scale_y_discrete]
# 年齢の整数部分だけを取り出し、離散値とし、さらにファクタとする
heightweight$ageYear.f = factor(floor(heightweight$ageYear))
## 各年齢の行数
table(heightweight$ageYear.f)
#11 12 13 14 15 16 17
#30 63 46 44 39 10 4
# 単に年齢(11〜17)の個数を数え上げたグラフ
## 横軸のxをファクタとして扱う。
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear.f))
gp = gp + geom_bar()
# 現在の状態はx軸は、11から17までの7つ
gp
# 順番を変える
gp + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("12","13","14","15","11","16","17"))
# 順番を反転させる
gp + scale_x_discrete(limits=rev(levels(heightweight$ageYear.f)))
# 一部のみを表示する
gp + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("12","13","14"))
# 軸のラベルに新しい名前を対応させる
gp + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("12","14","16"),
breaks=c("12","14","16"),
labels=c("Twelve","Fourteen","Sixteen"))
#スケールの変更
library(gcookbook) # 散布図を描画(xを年齢、yを身長) gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear,y=heightIn)) gp = gp + geom_point() # x軸とy軸を反転 gp + coord_flip() # x軸とy軸のスケールを同じにする。 gp + coord_fixed() ## y軸のスケールをx軸の2倍とする。 gp + coord_fixed(ratio = 1/2) # y軸の表示を対数表示に gp + scale_y_log10()
(3)凡例
準備
#使用するデータフレーム
library(gcookbook) # 離散値用のデータフレーム head(PlantGrowth) #. weight group #1 4.17 ctrl #2 5.58 ctrl #3 5.18 ctrl #4 6.11 ctrl #5 4.50 ctrl #6 4.61 ctrl # 行数は30 str(PlantGrowth) #'data.frame': 30 obs. of 2 variables: #$ weight: num 4.17 5.58 5.18 6.11 4.5 4.61 5.17 4.53 5.33 5.14 ... #$ group : Factor w/ 3 levels "ctrl","trt1",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... # grouopは要素数3のファクタ PlantGrowth$group #[1] ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl ctrl #[11] trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 trt1 #[21] trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 trt2 #Levels: ctrl trt1 trt2 # 連続値用のデータフレーム head(heightweight) # sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb #1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0 #2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0 #3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0 #4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0 #5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5 #6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0 str(heightweight) #'data.frame': 236 obs. of 7 variables: #$ sex : Factor w/ 2 levels "f","m": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... #$ ageYear : num 11.9 12.9 12.8 13.4 15.9 ... #$ ageMonth : int 143 155 153 161 191 171 185 142 160 140 ... #$ heightIn : num 56.3 62.3 63.3 59 62.5 62.5 59 56.5 62 53.8 ... #$ weightLb : num 85 105 108 92 112 ...
凡例の作成
# ボックスプロットの作成(fillは離散値groupにマッピング) ## 凡例は離散表現となる gp_dc = ggplot(PlantGrowth,aes(x=group,y=weight,fill=group)) gp_dc = gp_dc + geom_boxplot(); gp_dc # 散布図の作成(fillは連続値ageYearにマッピング) ## fillをプロットに反映させるには、塗りのあるshapeを選ぶ必要あり ## 凡例はカラーバーとなる gp_con = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb,fill=ageYear)) gp_con = gp_con + geom_point(size=3,shape=21); gp_con
凡例タイトル
# 離散値の凡例のタイトルを変更(デフォルトは軸名) gp_dc + scale_fill_discrete(name="Condition") #同じ gp_dc + labs(fill="Condition") #省略記法 # 連続値の凡例タイトルの変更 gp_con + scale_fill_continuous(name="Condition") #同じ gp_con + labs(fill="Condition") #省略記法
凡例ラベル
# 凡例のラベル(デフォルトは要素名)を更新
gp_dc + scale_fill_discrete(
labels=c("Control","Treatment 1","Treatment 2"))
## 要素数が不足しているところはNAとなる
gp_dc + scale_fill_discrete(
labels=c("Control","Treatment 1"))
# 連続値凡例のカラーバーの目盛と範囲を設定
gp_con + scale_fill_continuous(
limits=c(10,20), breaks=seq(10,20,by=5)
)
# 目盛に対応するラベルを更新
gp_con + scale_fill_continuous(
limits=c(10,20), breaks=seq(10,20,by=5),
labels=c("Ten","Fifteen","Twenty"))
# 離散値凡例の色をグレースケールで0.5〜1.0の範囲とする。
gp_dc + scale_fill_grey(
start=.5,end = 1,limits=c("ctrl","trt1","trt2"))
## カラーバーの最小値を黒、最大値を白とする
gp_con + scale_fill_gradient(
low="black", high="white",
limits=c(10,20),breaks=seq(10,20,by=5))
## カラーバーの代わりに離散的な凡例を用いる。
gp_con + scale_fill_gradient(
low="white", high="black",
limits=c(12,18),breaks=seq(12,18,by=3),
guide = guide_legend())
凡例の非表示
# fill凡例を非表示 gp_dc + scale_fill_discrete(guide=FALSE) gp_con + scale_fill_continuous(guide=FALSE) # 全てのエステてヒックマッピングを一気に非表示 gp_dc + theme(legend.position="none") gp_con + theme(legend.position="none")
凡例の位置を変える
# 上部に表示
gp_dc + theme(legend.position="top")
# 座標で指定:左下が(0,0), 右上が(1,1)
gp_dc + theme(legend.position=c(0.8,0.2))
# 凡例を4隅に合わせる
gp_dc + theme(legend.position=c(0,1),
legend.justification=c(0,1))
gp_dc + theme(legend.position=c(0,0),
legend.justification=c(0,0))
その他
# 凡例の枠に境界線をつける
gp_dc + theme(legend.background =
element_rect(fill="white",colour="black"))
# 凡例ラベルの体裁を一気に変更
gp_dc + theme(legend.text=element_text(
face="italic",family="Times",colour="red",size=14))
gp_con + theme(legend.text=element_text(
face="italic",family="Times",colour="brown",size=20))
(4)色パレットの利用
準備
# 連続値用のデータフレーム head(heightweight) # sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb #1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0 #2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0 #3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0 #4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0 #5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5 #6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0 str(heightweight) #'data.frame': 236 obs. of 7 variables: #$ sex : Factor w/ 2 levels "f","m": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... #$ ageYear : num 11.9 12.9 12.8 13.4 15.9 ... #$ ageMonth : int 143 155 153 161 191 171 185 142 160 140 ... #$ heightIn : num 56.3 62.3 63.3 59 62.5 62.5 59 56.5 62 53.8 ... #$ weightLb : num 85 105 108 92 112 ... # ageYearの少数部分を切り捨て heightweight$ageYear.i = floor(heightweight$ageYear) #[1] 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 11 13 ... # 年齢(ageYear.i)をファクタとする heightweight$ageYear.f = factor(heightweight$ageYear.i) #[1] 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 11 13 ...
よく使われる色パレット
# デフォルトのboxplot ## fillを指定していない場合、白色が塗られる。 gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear.f,y=heightIn)) gp + geom_boxplot() # 一律に色を塗る gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear.f,y=heightIn)) gp + geom_boxplot(colour="black",fill="purple") # エステティックマッピングでfillに軸名を対応させると # ファクトの要素ごとに異なる色の配色となる gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=ageYear.f,y=heightIn,fill=ageYear.f)) gp = gp + geom_boxplot() gp # デフォルトの配色パレット ## 色相で等距離にあるもの gp + scale_fill_discrete() gp + scale_fill_hue() #上に同じ # グレースケール gp + scale_fill_grey() ## 始まりと終わりのグレースケールの値を指定 gp + scale_fill_grey(start=1.0,end=0.5) # viridisパレット # library(viridis) gp + scale_fill_viridis_d() # ColorBrewerパレット(デフォルト) gp + scale_fill_brewer() ## ColorBrewerで使用できるパレットを調べる library(RColorBrewer) display.brewer.all() ## 引数でパレットを指定 gp + scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Oranges") gp + scale_fill_brewer(palette = "PiYG") gp + scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Paired") gp + scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set2")
手動で色を決める
# 手動で色指定(valuesで要素の数だけ指定します)
gp + scale_fill_manual(
values=c("purple","pink","purple","pink","purple","pink","purple"))
gp + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("12","16"),
labels=c("Twelve","Sixteen")) +
scale_fill_manual(values=c("#CC6666","#7777DD"))
Natureの色パレットを使う。
# そのほかによく使われているものとして、
# Nature Publishing Groupのパレットががあります。
# ggsciのライブラリを使用します。
install.packages("ggsci")
library(ggsci)
gp + scale_fill_npg()
(5)その他
タイトルの設定 [ggtitle]
# タイトルを設定する
ggtitle("Age and Height of Schoolchildren")
# 2番目の引数はサブタイトル
ggtitle("Age and Height of Schoolchildren","11.5 to 17.5 years old")
グラフを複数に分割する [facet_gird][facet_wrap]
# 使用するデータフレーム
head(heightweight)
# sex ageYear ageMonth heightIn weightLb
#1 f 11.92 143 56.3 85.0
#2 f 12.92 155 62.3 105.0
#3 f 12.75 153 63.3 108.0
#4 f 13.42 161 59.0 92.0
#5 f 15.92 191 62.5 112.5
#6 f 14.25 171 62.5 112.0
str(heightweight)
#'data.frame': 236 obs. of 7 variables:
#$ sex : Factor w/ 2 levels "f","m": 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
#$ ageYear : num 11.9 12.9 12.8 13.4 15.9 ...
#$ ageMonth : int 143 155 153 161 191 171 185 142 160 140 ...
#$ heightIn : num 56.3 62.3 63.3 59 62.5 62.5 59 56.5 62 53.8 ...
#$ weightLb : num 85 105 108 92 112 ...
# ageYearの少数部分を切り捨て
heightweight$ageYear.i = floor(heightweight$ageYear)
#[1] 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 11 13 ...
# 年齢(ageYear.i)をファクタとする
heightweight$ageYear.f = factor(heightweight$ageYear.i)
#[1] 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 11 13 ...
# 身長(x=heightIn)と体調(y=weightLb)の相関図をプロット
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb))
gp + geom_point(size=3, shape=21)
# 年齢で色分けする
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb,fill=ageYear.f))
gp = gp + geom_point(size=3, shape=21)
gp + scale_fill_discrete()
# 性別で色分けする
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb,fill=sex))
gp = gp + geom_point(size=3, shape=21)
gp + scale_fill_discrete()
# 要素ごとに異なるグラフを作成する(ファセットの利用)
## 基本プロットの作成
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb))
gp = gp + geom_point(size=3, shape=21, fill="black")
## 垂直方向に分割
gp + facet_grid(ageYear.f ~ .)
gp + facet_grid(sex ~ .)
## 水平方向に分割
gp + facet_grid(. ~ ageYear.f)
gp + facet_grid(. ~ sex)
## なるべく同じ行数列数で配置
gp + facet_wrap( ~ ageYear.f)
## 行数を指定
gp + facet_wrap( ~ ageYear.f, nrow=4)
## 列数を指定
gp + facet_wrap( ~ ageYear.f, ncol=4)
## xとyをフリースケールにする
##(軸の範囲が可変となります)
gp + facet_wrap( ~ ageYear.f, scales = "free")
## yのみをフリースケールにする
gp + facet_wrap( ~ ageYear.f, scales = "free_y")
# ファセットラベルのテキストを変更する
## 凡例ラベルと異なり、
## ファセットラベルを変更するには、
## 大元のデータフレームのデータを変更しなければな
# install.packages(dplyr)
library(dplyr)
# dplyrライブラリのrecode関数を使うと、
# 文字列を異なる文字列に一括に変換してくれます。
heightweight$gender =
recode(factor(heightweight$sex), "f"="Female","m"="Male")
## 次のように変わりました.
###[BEFORE]
heightweight$sex
#[1] f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f
#...
#[100] f f f f f f f f f f f f m m m
#...
###[AFTER]
heightweight$gender
#[1] Female Female Female Female Female Female
#...
#[109] Female Female Female Male Male Male
#...
## これでファセットラベルが「Female」「Male」となりました
gp + facet_grid(. ~ gender)
# ファセットラベルのサイズを変える
gp + facet_grid(. ~ gender) +
theme(strip.text = element_text(size=40))
# ファセットラベルの背景も変える
gp + facet_grid(. ~ gender) +
theme(strip.text = element_text(face="bold",size=rel(2)),
strip.background =
element_rect(fill="lightblue",colour="black",size=1))
# ファセットごとに異なる色を与える.
## fillを使いますが、判例とファセットで表記が重なるため,
## 凡例を消去します.
gp = ggplot(heightweight,aes(x=heightIn,y=weightLb,fill=gender))
gp = gp + geom_point(size=3, shape=21)
gp = gp + scale_fill_discrete(guide=FALSE)
gp + facet_grid(. ~ gender) +
theme(strip.text = element_text(size=40))
グラフ内のテキスト [geom_text]
# 特定の列名(連続値変数)の値を表示したいとき ## vjustで表示位置の調整、棒グラフの内側に表示(Weightは列名) geom_text(aes(label = Weight), vjust = 1.5, colour="white") ## 棒グラフの外側に表示 geom_text(aes(label = Weight), vjust = -0.2) # 特定の列名(カテゴリカル変数)の、各値(ggplotでx値にマッピングされているもの)の個数を表示させたいとき geom_text(aes(label=..count..),stat = "count", vujust = 1.5, color = "white") # ラベルの表示位置を各棒グラフ上端の少しだけ上側に表示する(Weightは列名) geom_text(aes(label = Weight, y = Weight + 0.1)) # ラベルの値を小数点以下の桁数を2桁に揃え、単位「kg」を追加する(Weightは列名) goem_text(aes(label=paste(format(Weight,nsmall=2),"kg"),size=4) # (x,y)=(4.5,66)に文字列「Group 1」をサイズ10で描画 geom_text(x=4.5,y=66, label="Group 1", size=10)
注釈 [annotate]
# (x,y)=(3,48)に文字列「Group1」を描画
anotate("text", x=3, y=48, label="Group1")
## フォントの属性も設定
anotate("text", x=3, y=48, label="Group1",
family="serif", fontface="italic",colour="darkred",size=3)
テーマ(グラフ全体の見栄え)の設定 [theme_xxx]
[参考]|ggplot2のテーマはどれを使うべきか
# デフォルトのテーマ theme_gray() # 背景の色が異なるなど、さまざまなテーマがある。 theme_bw() #枠線太め theme_dark() #背景暗め theme_light() #枠線細め theme_minimal() #枠線なし theme_void() #グリッドも枠線もなし theme_classic() #クラシックなやつ
テーマ関数の使用例 [theme()]
# x軸(縦方向)の目盛線を取り除き、Y軸(横方向)の目盛線を点線にする。 theme( panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(), panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank(), panel.grid.major.y = element_line(colour="grey60",linetype="dashed")) # タイトルの中に移動する theme(plot.title = element_text(just = -8)) # タイトルの各種設定 ## サイズは基本フォントサイズの1.5倍 ## lineheightは行間の設定 theme(plot.title = element_text( size = rel(1.5), lineheight=0.9, family="Times", face="bold.italic",colour="red")) # X軸のラベルを60度傾ける theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=60,hjust = 1)) # X軸のラベルのフォントを設定する。rel(0.9)はベースフォントに対して0.9倍の意 theme(axis.text.x = element_text(family="Times",face="Italic",colour="darker",size=rel(0.9)) # X軸のタイトルを取り除く(タイトル領域がなくなる) theme(axis.title.x = element_blank()) # 横方向のメモリを除き、判例の位置(position)とアンカー位置(justification)を設定 theme( panel.grid.major.y = element_blank(), legend.position = c(1,0.55), legend.justification = c(1,0.5) ) # 両軸の目盛記号を非表示にする。 theme(axix.ticks=element_blank()) # 目盛のラベルだけ非表示にする(y軸) theme(axix.text.y=element_blank())